
Gravitational Attraction
What would happen if two people out in space a few meters apart, abandoned by their spacecraft, decided to wait until gravity pulled them together? My initial thought was that …

What would happen if two people out in space a few meters apart, abandoned by their spacecraft, decided to wait until gravity pulled them together? My initial thought was that it would take a really long time, longer than they would practically be able to wait. The calculation (unless I've done something wrong) seems to indicate otherwise.
My first approach, which is approximate, is to determine the resulting kinetic energy when they come together and assume (badly) that it was a constant acceleration to determine the time. This will low-ball the time but be easy to calculate. My second approach is to numerically simulate the system in pyndamics3. If I feel like it, I might do the integral later, but after the first approximation I like to look at things numerically (mostly for fun).
Let's make the following assumptions:
then we set up the calculation
In [7]: G=6.7e-11
In [8]: m1=100
In [9]: m2=100
In [10]: r_start=3
In [11]: r_end=0.5
In [12]: -G*m1*m2/r_start-(-G*m1*m2/r_end)
Out[12]: 1.1166666666666668e-06
In [13]: v=sqrt(2*1.12e-6/(m1+m2))
In [14]: v
Out[14]: 0.00010583005244258362
Assuming a constant acceleration, for each person to travel half of the 2.5 m distance separation, would be
which is much shorter time than I was expecting!
Not being satisfied, I implemented it in [pyndamics3]
from pyndamics3 import *
sim=Simulation()
sim.add("x1' = v1",-1.5,plot=True)
sim.add("x2' = v2",1.5,plot=True)
sim.add("v1' = G*m1*m2/(x2-x1)**2/m1",0,plot=True)
sim.add("v2' = -G*m1*m2/(x2-x1)**2/m2",0,plot=True)
sim.params(G=6.7e-11,m1=100,m2=100)
second=1
minute=60*second
hour=60*minute
day=24*hour
t=13*hour+25*minute
sim.run(t)
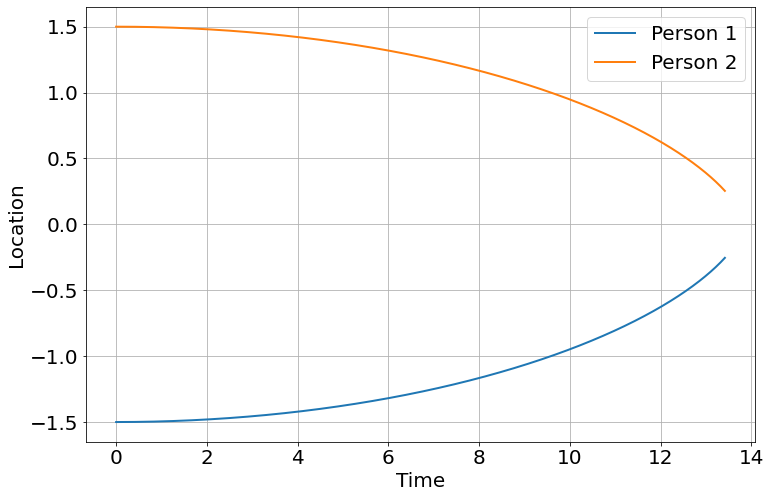
which clearly shows them coming together in around 1/2 of a day, from their own gravity. I guess I have to adjust my intuitions for such situations.